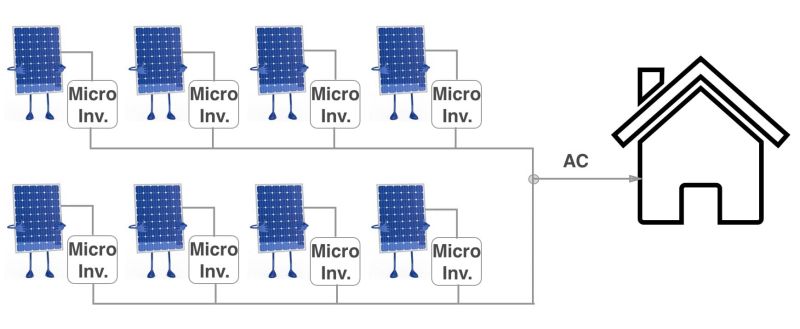
Micro-inverters are a type of solar inverter that is installed on each individual solar panel, as opposed to a central inverter that handles the entire solar array. Here’s how micro-inverters work:
1. Individual conversion: Each solar panel in the system has its own micro-inverter attached to it. The micro-inverter converts the DC power generated by the panel directly into AC power.
2. MPPT tracking: Similar to traditional inverters, micro-inverters also perform Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). They continuously monitor panel output and adjust the conversion process to maximize the power output of each individual panel.
3. AC output: Once the DC power is converted to AC by the micro-inverter, it can be used immediately by electrical devices in the building or exported to the grid.
4. Individual monitoring: Micro-inverters typically come with built-in monitoring features. These allow system owners to monitor the performance of each individual panel in real time, including energy production, voltage and other parameters. This granular monitoring capability helps with system troubleshooting, maintenance and identification of under performing or faulty panels.
5. Security benefits: One of the key benefits of micro-inverters is their enhanced safety features. Because each panel has its own micro-inverter, there is no high DC voltage on the roof or in the system, making it safer for installers, maintenance personnel and firefighters.
6. Scalability and flexibility: Micro-inverters offer scalability because additional solar panels can be easily added to the system without worrying about system-level limitations. They also offer flexibility in system design, as panels can be installed in different orientations and tilt angles without affecting the overall performance of the system.
In addition, micro-inverters are known for their ability to improve overall system performance. Because each solar panel has its own micro-inverter, the performance of one panel does not affect the performance of other panels in the system. This is in contrast to central inverter systems, where shading or dirt on one panel can significantly reduce the output of the entire array.
The micro-inverters are often designed to be more efficient than traditional central inverters. They minimize the power losses associated with conversion by performing the DC to AC conversion directly at the panel level. This results in higher overall system efficiency and increased energy production.
Micro-inverters also offer easier maintenance and troubleshooting. With central inverters, it can be difficult to locate the source of a problem if it affects the entire system. In contrast, micro-inverters allow individual panels to be monitored, making it easier to identify and replace under performing or faulty panels. This targeted approach to maintenance results in better system uptime and optimized energy production.
Finally, micro-inverters can be a more aesthetically pleasing option for solar installations. Central inverters typically require more space to accommodate their size and cooling requirements, while micro-inverters can be easily integrated into the solar panel frame, reducing the visual impact.
Conclusion
In short, micro-inverters provide a reliable and efficient solution for solar power generation. With panel-level conversion, enhanced safety features, scalability, flexibility and higher performance, micro-inverters offer advantages over traditional central inverters, from increased energy production and system efficiency to improved safety and simplified maintenance, making micro-inverters a reliable and versatile solution for residential and commercial solar installations.
Post time: Aug-29-2023